Android ListView Advanced
23 Apr 2013Introduction
ListView is one of the most fundamental and important Android UI components. Due to the long rectangle shape of mobile device, ListView is widely used as the first level navigation to the more detailed content. Popular using scenarios include, but not limited to, news reader, reading list, e-commere product list, things to do list, ranking list, etc. If your applicaiton intends to providing updatable contents to users, you cannot avoid using this super powerful widgets.
ListView can be very simple and also extremely complex. There are many traps and tricks for novice developers. In this article, the author will summerize some typical traps developers may occur during their use of ListView and try to provide solutions or suggestions. In more general, the author will summerize typical advanced usages of ListView, such as pull to refresh ListView, HTTP cache, data binding, loader, etc.
Simple Example
Android ApiDemos Sample provide a bundle of examples for using ListView (under android-sdk-macosx/samples/android-17/ApiDemos/src/com/example/android/apis/view).
The following is a simple example.
- /Users/lucas/dev/eclipse-juno-workspace/AdvancedListView/src/com/example/android/apis/view/advancedlistview/SimpleListViewActivity.java
package com.example.android.apis.view.advancedlistview;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
public class SimpleListViewActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_simple_listview);
ListView lv = (ListView) this.findViewById(R.id.list);
ListAdapter adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, COUNTRIES);
lv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private static String[] COUNTRIES = new String[] { "CHINA", "US", "JAPAN" };
}
- /Users/lucas/dev/eclipse-juno-workspace/AdvancedListView/res/layout/activity_simple_listview.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</RelativeLayout>
This is a very simple example of ListView.
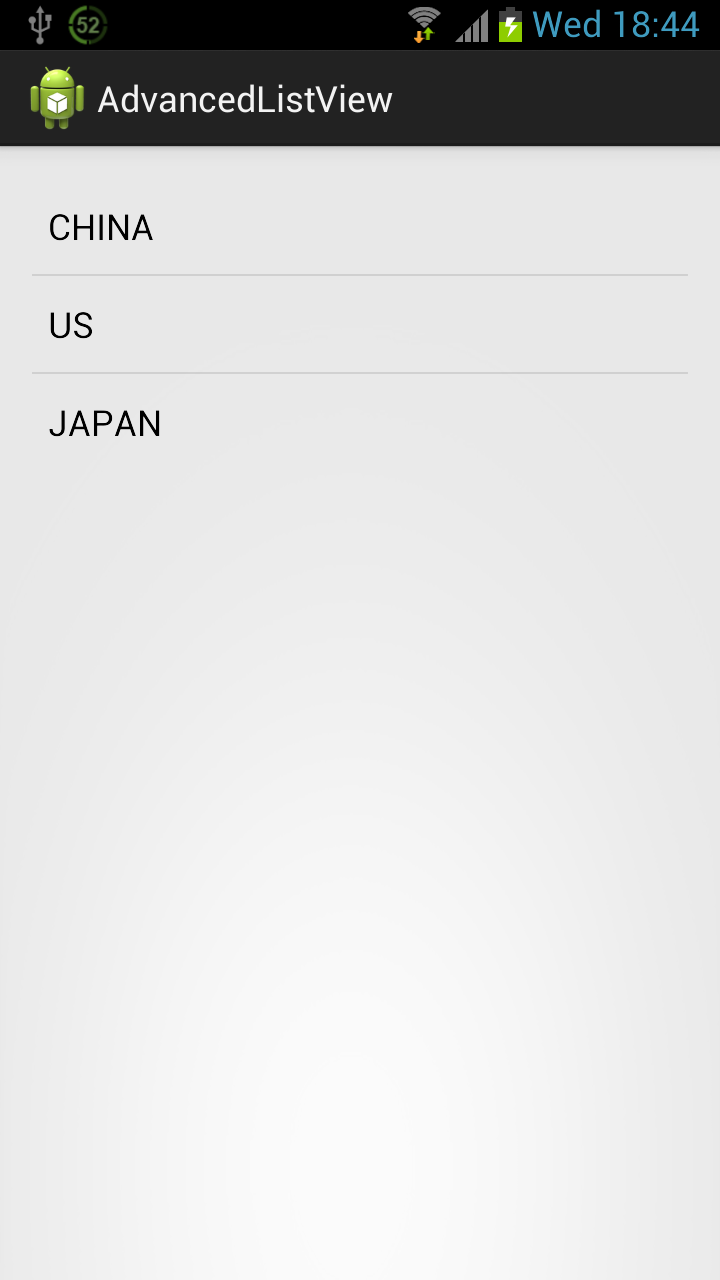
Adapter Architecture
From the above simple example, we find 3 components for the ListView: the standard MVC pattern. Model, View, and Controller.
View
ListView is embeded in Activity in layout XML.
Data
To provide data for each item in the ListView, we need a Adapter. Here we use ListAdapter, constructed from a static String array.
Controller
If you want users to interact with your app, you can add Listeners for user actions, for example, click event, touch event.
This can be done by setting setOnItemClickListener.
Framework API
Official Tutorials
- Official introductory tutorial can be found at this link.
- Building Layouts with an Adapter
Non-Official Tutorials
API Explored
Performance
Reusing
ConvertView
ViewHolader
Header & Footer
Load Data Async
Data Binding
HTTP + JSON
Image
GroupList/ SectionList
Resources on Github
问题
- Occasionally, you get the
IllegalStateExceptionerror, stating“The content of the adapter has changed but “ + “ListView did not receive a notification. Make sure the content of “ + “your adapter is not modified from a background thread, but only from “ + “the UI thread. Make sure your adapter calls notifyDataSetChanged() “ + “when its content changes. “
By checking the source code, we find that when the ListView’s ‘mItemCount’ is different from the bound adapter’s count, framework will throw the exception.
Here ‘mItemCount’ is written when the adapter is first time set or when ‘onMeasure’ is called (refresh).
<img src=”imgs/listview_itemcount_write.png”.
// Handle the empty set by removing all views that are visible
// and calling it a day
if (mItemCount == 0) {
resetList();
invokeOnItemScrollListener();
return;
} else if (mItemCount != mAdapter.getCount()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The content of the adapter has changed but "
+ "ListView did not receive a notification. Make sure the content of "
+ "your adapter is not modified from a background thread, but only from "
+ "the UI thread. Make sure your adapter calls notifyDataSetChanged() "
+ "when its content changes. [in ListView(" + getId() + ", " + getClass()
+ ") with Adapter(" + mAdapter.getClass() + ")]");
}
- Performance Tips for Android’s ListView
- [Google I/O 2010 - The world of ListView]<iframe width="560" height="315" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/wDBM6wVEO70" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>